4) Number Before
Counting: Lesser Number
Counting Review
Activities 1 to 5: These boards have been superseded by the Bond Blocks Counting to 10 & 20 Kit but remain for revision of Foundation counting.
Mathematics
- Develop fluency identifying the number before, for numbers up to ten.
Representing the number after on a number track.

For example, the number after five.

Representing the number before on a number line.

For example, the number before five.

Language
- number before
- one less than
- one fewer than
When initially completing the activity introduce and use the language “the number after”. In subsequent sessions, once students are fluent with the activity, change the language to “one greater than” and later still “one more than”.
Mental Number Lines
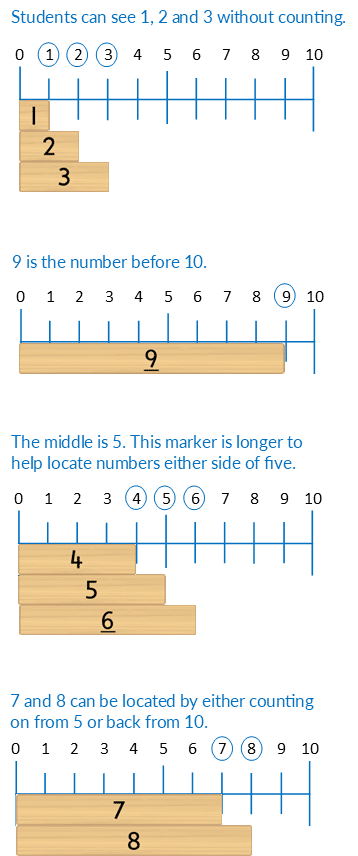
One use for number lines is counting forwards and backwards. For example, forwards from zero or backwards from ten. Please note, this is not how the number lines are to be used in these activities.
In these activities number lines are used to develop the concept of a mental number line, that is, where numbers are located in relation to each other. If students need to count to identify the location of a number they should only count on/back one, two or three. Counting more than this is inefficient, error prone and limits opportunities for students to develop more effective strategies.
- Activity 2 focuses on locating the number after.
- Activity 4 focuses on locating the number before.
- As students progress through the Bond Blocks system they will develop the skills needed to locate harder to identify numbers such as 7 and 8.

Differentiation
A little easier
Scaffold: alternating numbers
Remove every second block from the steps. Build flat on a desk. Students count aloud, pointing to each number as it is said.

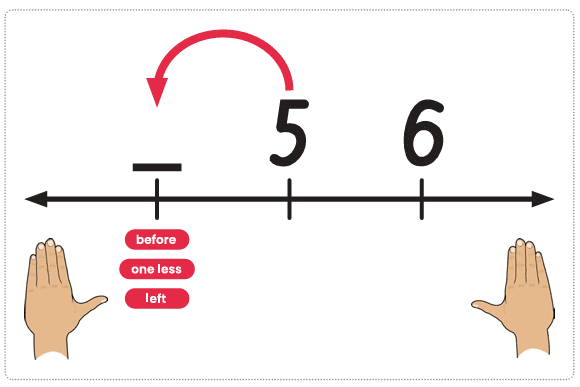
Next, repeat this activity but the student takes turns saying the counting numbers with the teacher. The teacher points to and says the number that is represented with Bond Blocks. The student points to the space before this block and says the number that is missing.

Then, repeat counting with alternating numbers, taking turns with the teacher, but introduce the language, “The number before”. The teacher points to the Bond Block that is placed and says, “The number before ten is…” The student points to the space after Block Ten and says “Nine.”

Once students are fluent using the alternating steps made with even numbers repeat using the odd numbered Bond Blocks.
Directional Support: desk visual
Mathematics is different to English. When teaching reading English fluency moving from left to right is stressed. Mathematics requires students to be fluent moving in many directions. Consider:
- Horizontal movement on a number line. Move right to count forwards, add, and increase the value of numbers. Move left to count backwards, subtract by taking away, and reduce the value of numbers.
- The place value chart is opposite to this. Values increase to the left and decrease to the right.
- Addition and subtraction strategies. When adding and subtracting mentally it is often easier to use place value and work from left to right. However, when adding, subtracting and multiplying using an algorithm calculations are completed from right to left. The division algorithm is completed in the opposite direction.
- Vertical movement on a number line as per a thermometer or y-axis on a graph.
- Diagonal and curved movement as per a line or parabola.
- Rotations clockwise and anticlockwise.
Click to download a Directional Support: Desk Visual to support students who have directional and sequencing difficulties.
A little harder
Counting: number before
Complete the ‘a little harder’ activity board.
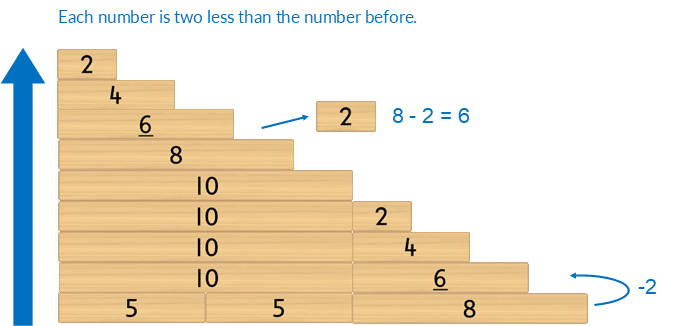
Counting: even steps
Count backwards, subtracting two each time, starting at 10, with blocks, to 2.

Extend to counting backwards with even numbers, by two, from 18.
Count backwards, subtracting two each time, starting at 10, without blocks, to 2. Extend to counting backwards by two, without blocks, from 18.
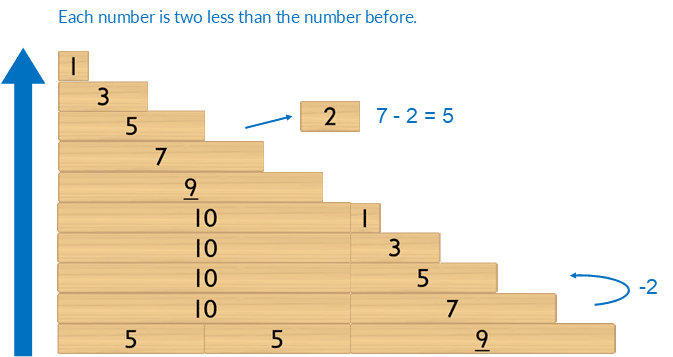
Counting: odd steps
Count backwards, subtracting two each time, starting at 9, with blocks, to 1.

Extend to counting backwards with odd numbers, by two, from 19.
Count backwards, subtracting two each time, starting at 9, without blocks, to 1. Extend to counting backwards by two, without blocks, from 19.
Counting Practice: fluency packing away
Develop fluency counting backwards when packing away. Cover the template with a piece of white paper that is 22cm x 20cm.
Give students a different instruction each time they pack away. For example:
- Pack away the even blocks first.
- Pack away the odd blocks first.
- Pack away the even blocks first, starting at 10, counting backwards.
- Pack away the odd blocks first, starting at 9, counting backwards.
Progression
In the next activity students identify individual numbers in the counting sequence to 10 without counting. Go to
Activity 5
Counting: Identifying Numbers 6 to 10, Building Steps
